Resource Navigation
DFSS (Design For Six Sigma)
03
February,
2023
3 MINUTE READ

What is DFSS (Design for Six Sigma)?
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) is a process for bringing new products to market with a performance of 4.5 sigma or better (that is, practically no defects) This requires understanding what customers require, what they value, and what they are willing to pay for. It involves having a deeper understanding of customers than just knowing the types of products they want. For example, say a major component fails and the customer requests a direct replacement; if you propose a replacement that also improves efficiency, you've met the customer's stated need as well as an unstated need, delivering greater value to the customer.
DMAIC or DMADV?
DMAIC is the approach most closely associated with Six Sigma. It provides a framework for identifying problems in an existing process or product, correcting them, and then verifying they have been corrected. DMAIC stands for:
- Define the problem and goals
- Measure the process' effectiveness
- Analyze the information and identify defects
- Improve the process to eliminate defects
- Control the process.
However, DMAIC is a methodology for improving current products and processes. So what can businesses use when they need to create a new product or process?
DMADV is a common Six Sigma approach for designing new products. DMADV stands for:
- Define design standards. This includes identifying who the customers are, what their needs are, and whether those needs can be met by a product or service your company can produce.
- Measure and identify the specific characteristics the product needs to have, as well as the characteristics and features the customers do not want.
- Analyze the data resulting from the previous step. Use this information to propose possible designs, and identify possible sources of defects, as well as problems that could result in the customer's requirements not being met.
- Design the product, service, or process to meet the customer's needs.
- Verify that the design will meet all of the requirements.
There are a number other methods that can be used to support DFSS, such as IDOV. This approach consists of four phases:
- Identify ? gather data on the Voice Of the Customer (VOC) and conduct competitive analyses to identify opportunities.
- Design ? work from the basic design and performance requirements to produce several designs.
- Optimize ? select a design, develop its details, and then optimize the design.
- Verify ? test the selected design and use the feedback to make further design improvements
Using either DMADV or IDOV, companies can effectively apply Design for Six Sigma in the workplace. These methodologies provide a systematic method for designing products that will improve overall customer satisfaction by creating products that meet their expectations.
Design for Six Sigma Objectives
Whatever approach is used for DFSS, the objective is to identify value that the customer is willing to pay for and to match those needs with the needs of your business. For example, if your company makes molded plastic cases and would like to expand production, looking at the needs of potential customers who need left-threaded stainless steel widgets might not make a good match. However, if the potential customers also need heat resistant plastic cases for their widgets, then you can use DFSS to create an ideal product and meet specific needs.
Define
The first step in the DFSS process, defining the standards, is where many projects run off the rails. For example, suppose we want to make the best heat resistant plastic case that has ever been made. We might start designing a heavy-duty poly-carbonate case that can withstand temperatures as high as 250 ?F.
However, the customers may only need a case to resist temperatures up to 170 ?F, and it would be wasteful and overly expensive to design a case to withstand 250 ?F. The first step requires companies to identify the needs of the market and establish the design standards based on those needs.
Measure, Analyze, and Design
The next three steps involve quantifying what customers need, as well as what they do not want. In our example, the casing may need to be heat resistant, but only up to 170 ?F; it must be red; and it cannot weigh more than 20 ounces. The goal is to create a product the customer needs without adding extra costs, resulting from features, capabilities, or characteristics that the customer does not value. A second goal of this phase is to determine whether the product can be produced and sold profitably.
Accomplishing this may require specialized tools. For example, it may be necessary to create simulations or use parametric design tools to predict costs and performance. Tools may also be needed to model and predict the manufacturing process; the delivery system; and the logistics, facilities, and training needed to deliver the product to the customer.
Verify
In this step, the product design is tested to verify that it meets the identified requirements. This may involve building a prototype, conducting design reviews, and testing the prototype. Tests may be done completely in-house, may involve your customers, or may even involve your customer's customers. The objective is to "stress test" and debug the product. In our example, customers may want special features that make the casing extremely easy to use. This step will help identify needs that were not covered by the original design.
The final result is a quality design and a plan for full production and delivery of the product. The DFSS process should be completely documented, including all data, findings, and recommendations. This information is needed for the implementation of production, as well as to form the basis for the next generation of the product.
Design for Six Sigma Solutions
As mentioned earlier, DFSS may draw on a variety of methods to accomplish its objectives. Whether those methods involve Kanban, DMADV, or some other approach, Duralabel offers an array of lean manufacturing resources that can help get you started. Our resource center contains best practice guides, articles and infographics that can help you design products that meet the needs of your customers.
RELATED RESOURCES

Six Sigma Principles that Align with 5S
What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma is a systematic approach to eliminating errors that harmonizes with 5S and 5S ...
Read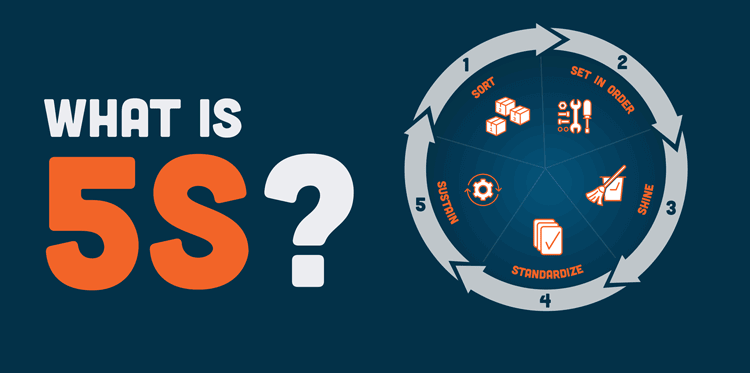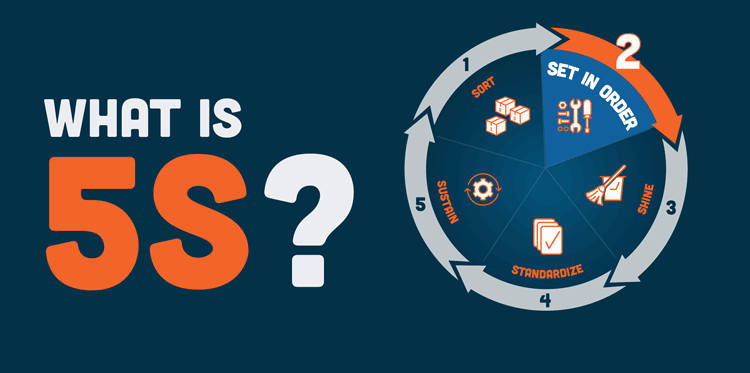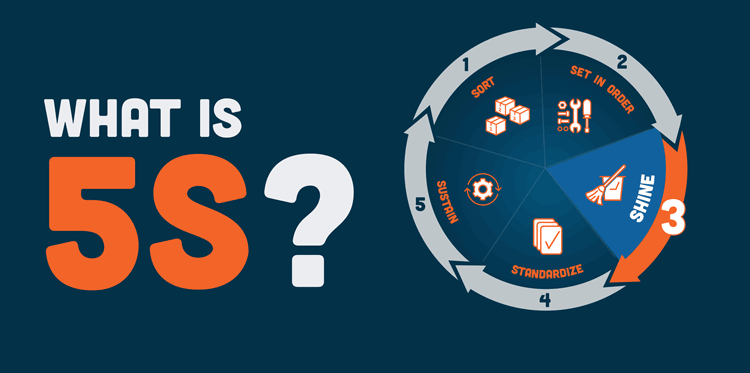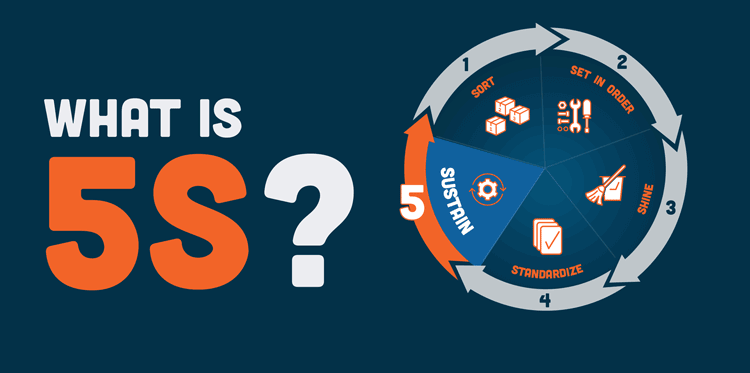
The 5S System Explained: From Origins to Implementation
What Is the 5S System? The 5S system is a lean manufacturing tool that improves workplace efficiency and ...
ReadPolychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
What Are Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)? Think of yourself as a lab rat. Chemicals synthesized in a ...
Read.png)


