- Home
- >
- Resources
- >
- Infographics
- >
- PPE Infographic
PPE Infographic
03
February,
2023
2 MINUTE READ
Equipment that is worn to limit exposure to harmful substances or dangerous conditions is known as PPE (personal protective equipment). It is designed to protect an employee against hazards including impact, temperature, harmful chemicals, dust, and others.
The following is a transcript of the PPE Infographic:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is geared for individual safety while performing any type of potentially hazardous work. Available PPE ranges from safety glasses, hard hats, gloves and lab coats, to HazMat suits, respirators, and more. Follow along to identify types of equipment used to protect individuals from injury or illness.
Head & Hearing Protection
Head protection (a hard hat) is required when engaged in hazardous work such as construction, tree trimming, or under catwalks. The potential danger of a falling object, electrical shock exposure or burn to the head requires a Class A, B, or C hard hat. Protect your ears from noise and vibrations that can permanently cause hearing loss while on the job. Refer to OSHA's publication 3074 (2002) to understand what sound level in decibels is permissible. Hearing protection options include: Single-use earplugs, pre-formed or molded earplugs, and earmuffs.
Torso Protection
High visibility safety vests and aprons may protect against hazards, such as chemical splashes, and low-light situations. Lead aprons and shielding help prevent radiation exposure.
Foot Protection
From energized electrical conductors that may come into contact with the feet, to falling or rolling objects, or objects that could pierce through the sole; footwear must comply with the ANSI 7-14-1991 standards. Toe guards, combination foot and shin guards, electrical conductive, or electrical hazard, and safety-toe footwear, may be required depending on the work engaged.
Eye & Face Protection
Appropriate eye and face protection, such as safety glasses, goggles, and face shields, must be used to protect against the hazards associated with flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids and caustic liquids, chemical gases and vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.
Respiratory Protection
Respiratory protection should be used to protect against inhalation hazards of chemical and physical properties when engineering and administrative controls are not adequate. Choose either air-purifying or atmosphere-supplying respirators depending on the toxicity and concentration of the hazardous material.
Hand Protection
The working environment will help determine which type of hand protection must be worn to protect against:
- Harmful substances
- Synthetic gloves
- Severe cuts, punctures, abrasions, or lacerations
-Leather, canvas, or metal mesh gloves
- Chemical burns & thermal burns
- Aramid fiber gloves
- Harmful temperature extremes
- Aluminized gloves
What Can Be Done to Ensure Proper Use of PPE?
Personal protective equipment must be designed and constructed specifically for safety. PPE is required to be worn in appropriate sizing, used as intended, and maintained in a clean and reliable fashion. Ensuring proper care and easy access to PPE can be the difference between a dangerous exposure and working safely.
84% of employees who sustain a head injury are not wearing head protection
50% of construction workers will suffer a serious eye injury during their career
99% of noise-induced hearing loss is preventable if proper hearing protection is used
25% of all workplace accidents involve hands and fingers
25% of all reported disabling injuries involve foot injuries
RELATED RESOURCES

Near-Miss Reporting
When is a close call more than a close call? It's important to reflect on near-misses and use their lessons ...
Read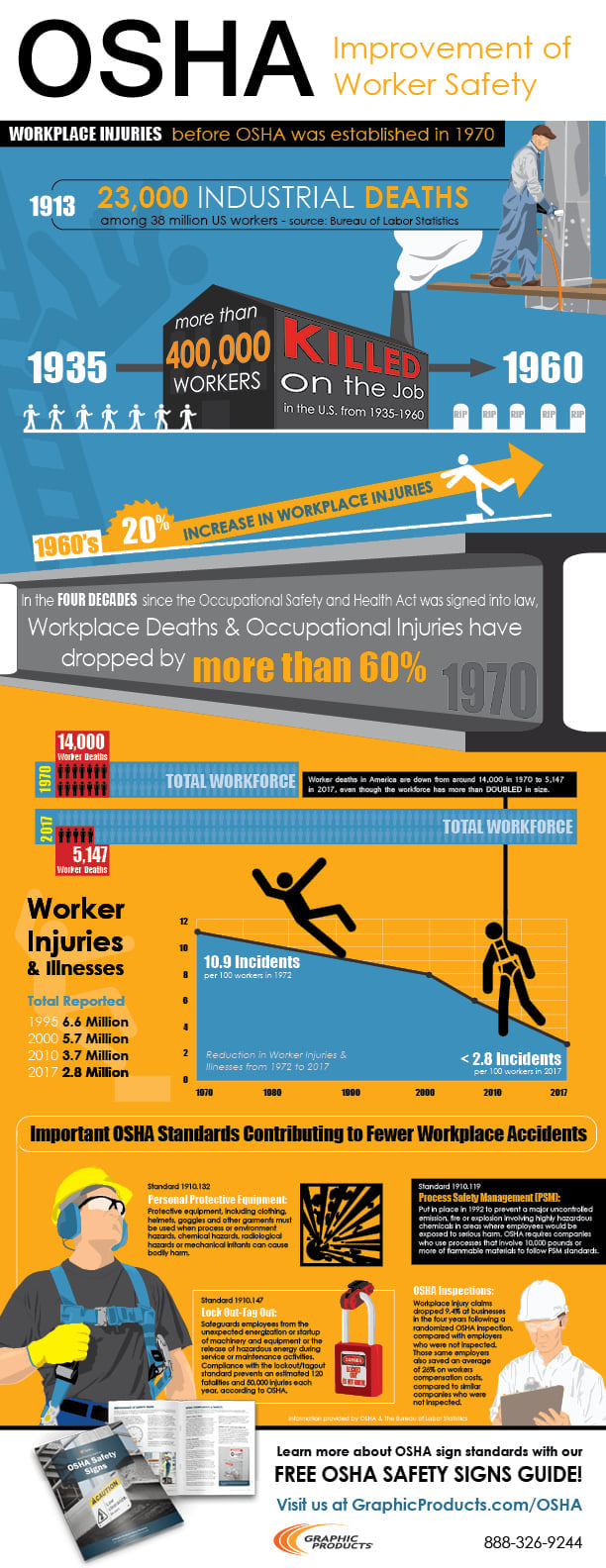
OSHA Improving Worker Safety
In 1970, OSHA was established to create standards that keep workers safe. Since 1970, workplace accidents and ...
Read
Food Manufacturing Safety
The food processing and manufacturing industry has come a long way since Upton Sinclair wrote and released ...
Read.png)



